© 2006 All Rights Reserved. Do not distribute or repurpose this work without written permission from the copyright holder(s).
Printed from https://danginteresting.com/the-only-nazi-aircraft-carrier/
In no naval action of World War 2 will you find a German aircraft carrier taking part. All the major navies in the war used them extensively, except for Nazi Germany. There were lots of German U-Boats, battleships, cruisers, and destroyers, but no flattops. However, the Nazis had plans to build a total of four carriers and almost finished one of them.
Her name was the KMS Graf Zeppelin and though launched in December 1938 she was never over 80% completed. Construction delays, lack of aircraft, and bitter disputes between Air Marshall Herman Goering and the Navy insured that the ship was doomed to become scrap metal.
Hitler had promised the German Navy (The Kriegsmarine) carriers as early as 1935, and the keel was laid for the Graf Zepplin on December 26, 1936. The Graf Zeppelin was 920 feet long and weighed 19,250 tons. Her top speed was to be 33.8 knots. Her crew complement was 1,760 and she was to hangar forty aircraft. By comparison the large American Essex class carriers of WWII could carry 80 to 100 aircraft. The Germans got as far as partly installing the catapults when the ship was then turned into a floating warehouse for u-boat parts.
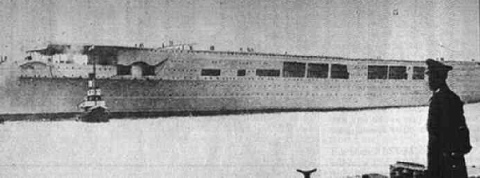
Hitler’s attitude vacillated on the project and it never had his full backing. It also had a major detractor in Goering, who was resentful of any incursion on his authority as head of the country’s air power. Goering had been ordered by Hitler to develop aircraft for the ship. His response was to offer redesigned versions of the then-obsolete JU-87 Stuka dive bomber and older versions of the Messerschmitt 109 fighter. Both planes were land-based aircraft never intended to meet the rough requirements for carrier operations. Even after modifications they were hopelessly inferior to Allied types. To insure further delay in the carrier’s completion, Goering informed Hitler that these planes would not be ready until the end of 1944. Goering’s tactics worked and the Graf Zeppelin’s construction was halted in 1943.
By the time work stopped on the ship, the Germany Navy had a submariner as its top naval officer— Admiral Karl Donitz— and all ship construction was turned over to building new U-Boats. The Graf Zeppelin stayed at her moorings in Stettin for the rest of the war never to see action.
As the end of the war in Europe neared, the Graf Zeppelin was scuttled in shallow water off Stettin (now Szczecin in Poland) on April 25, 1945 just before the Red Army captured the city. But she wasn’t quite ready for the scrap yard yet. According to recently found material in Russian archives, the ship was refloated by the Russians and towed to Leningrad filled with captured booty and military parts for use in the Soviet Union. After unloading her cargo she was named “PO-101” (Floating Base Number 101) by the Soviets. The new owners had hoped to repair and refit the ship as a new carrier but this proved to be impractical so the Graf Zeppelin had one more task to fulfill.

On August 16, 1947 she was towed out to sea and used for target practice by Soviet ships and aircraft. Aerial bombs were placed in her hangers, flight deck and smoke stack. Planes and ships then shot shells and dropped bombs on her to demonstrate how to sink a carrier, presumably American. After twenty-four hits the Graf Zeppelin stayed afloat and had to be finished off by torpedoes.
Details on how the Nazis planned to use the carrier in action have been lost to obscurity. The Germans had none of the experience that the American, British and Japanese navies had gained in the years between the wars. While the Graf Zeppelin had some advanced features she displayed her designers’ lack of knowledge about carriers. The heavy surface armament was of little use and accounted for too much weight; the anti-aircraft armament was heavy but badly sited, all on the starboard side. The radius of action was low for a fleet carrier intended to operate with the capital ships on the Atlantic shipping routes.
Had she been commissioned she would have provided a considerable commerce-raiding capability. The carrier could have provided effective support for capital ships and cruisers with air cover, and would have increased their potential for destruction considerably. Such support operations could have changed the outcome of sea battles like the sinking of the Battleships Bismarck and Tirpitz had the Graf Zeppelin been present.
The Germans have never sailed an aircraft carrier since.
© 2006 All Rights Reserved. Do not distribute or repurpose this work without written permission from the copyright holder(s).
Printed from https://danginteresting.com/the-only-nazi-aircraft-carrier/
Since you enjoyed our work enough to print it out, and read it clear to the end, would you consider donating a few dollars at https://danginteresting.com/donate ?